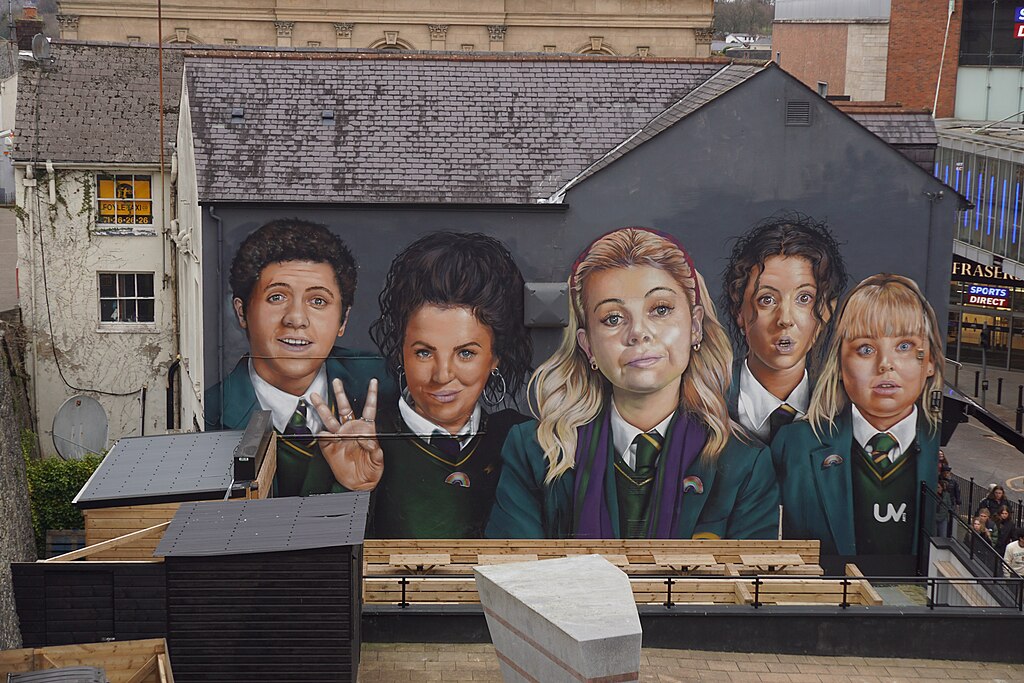

What can we learn from the hit show, Derry Girls? (If you have not seen this, run off and start watching now!) Derry Girls is an Emmy-winning comedic coming-of-age series set in Northern Ireland. The show follows spirited teenagers navigating adolescence amidst a backdrop of political conflict. The show is set in the 1990s, before the Belfast/Good Friday Agreement that brought an “official” end to the Troubles. Today, Northern Ireland experiences a fragile peace. Yet, many themes behind the comedy still hold true for teens in Northern Ireland today.
Like the show, adolescents in Northern Ireland navigate history, culture, and the complex interplay between tradition and modernity. Our research team[1] is currently exploring how these teens learn and share their “truths,” which often are polarized by ethno-religious identity (Catholic/Protestant). We argue that a holistic approach is needed to study how polarized information is transmitted through traditional, structurally embedded narratives and systems that intersect with new information sources and modern values. We discuss novel methods that can begin to embrace these complexities, as now more than ever, information (and misinformation) are readily available literally at teens’ fingertips.
There is a large field of research in developmental psychology focussed on how young people learn information from others. We know that young people exhibit epistemic vigilance; that is, they are motivated to seek reliable information and bridge gaps in their knowledge. However, young people (like all people) also exhibit biases in their information seeking and sharing. As early as infancy, children prefer to learn from members of their own social or cultural groups, and take group membership into account when deciding with whom to share information. Children absorb and transmit information that aligns with the values of their community. This important area of study sheds light on the cognitive and social processes involved in children’s early understanding of information reliability at the individual-level.
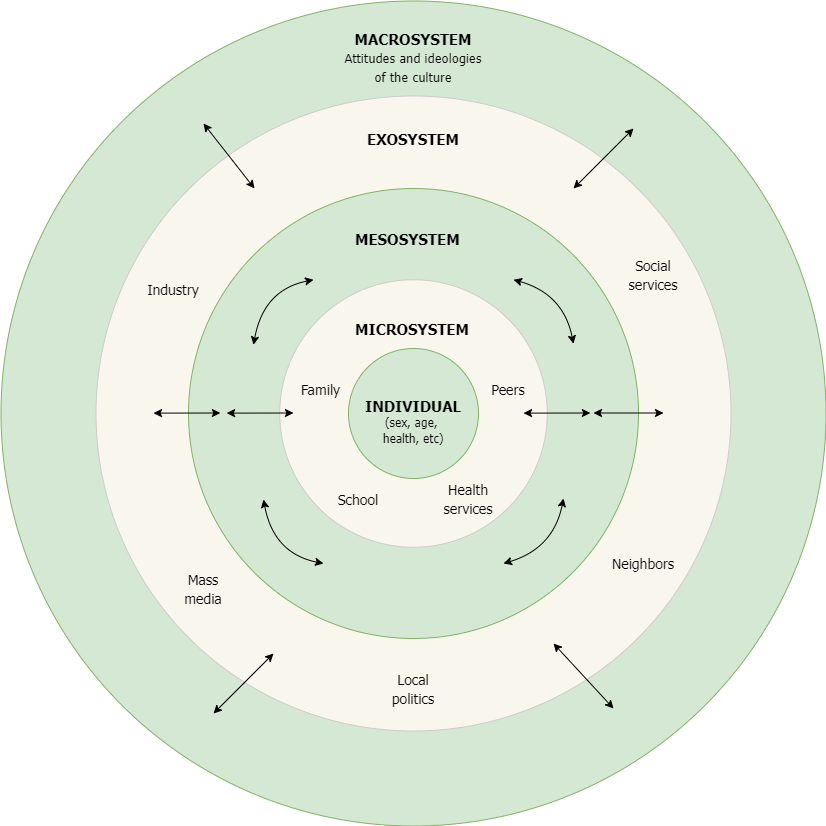
However, these findings currently lack perspective on how influences outside the individual, such as families, peers, schools, public policies, and cultural values, can combine to create a complex web of biases that shape the narratives young people construct about their communities. The socio-ecological framework (see, for example, Bronfenbrenner 1977) is a way of thinking about how different aspects of young people’s lives, from personal to societal to cultural, influence each other. The framework considers how individuals are shaped by their relationships, communities, and the larger society, as well as how they, in turn, can impact these environments. Using this framework, we can begin to elucidate how the push and pull of traditional post-conflict narratives and societal structures intersect with young people’s modernizing identities and values.
So, what can we learn from Derry Girls?
In episode 1 of season 2, the Derry girls participate in an attempt to mix their Catholic, all-girls school classroom with a classroom from a neighboring school of Protestant boys. A well-meaning but not-so-competent priest attempts to demonstrate overarching humanity through a brainstorming session of similarities across the mixed-background group. But alas, the failed exercise results in a full blackboard of “differences” between Catholics and Protestants, and an empty blackboard of “similarities.”

This replica of the now famous blackboard is on display at the Ulster Museum in Belfast, Northern Ireland. The show presented these stereotypes in a light-hearted, comedic way, but unfortunately, stereotypes of Catholic and Protestant identity contribute to polarized narratives still today. To highlight the necessity of investigating the development of polarization and epistemic vigilance within young people’s broader ecological frameworks, we provide two examples from this episode of Derry Girls. These examples demonstrate how societal processes seemingly interact with individual-level social cognitive processes.
Intergroup Competition
One “difference” suggested by the teens on the above blackboard is “Protestants are rich and Catholics are poor.” This common yet polarizing cultural narrative demonstrates the impact of a long history of zero-sum conflict and power dynamics across the island of Ireland. Historic narratives may enter into present day interactions with the “other.” For instance, in this episode Michelle, a Derry girl, says, “…I don’t see why we have to get them [Protestants] a present? I mean they already have all the land, all the jobs, and all the f***in’ rights.” This macro-level narrative of competition is upheld by contested symbols (like the “Free Derry” mural in the backdrop of many scenes in the show) in teens’ local communities, a micro-level influence. Take another micro-level example—when the Derry girls and “their” Protestants get into conflict, the dialogue immediately escalates into a polarizing narrative, e.g. “because all Protestants are the same.” Such intergroup competition across the ecological system may disrupt teens from seeking reliable epistemic cues, further fostering a preference for ingroup information, even when that information is likely unreliable. (How many Protestants actually keep toasters in the cupboard?)
Segregation
“Why is everyone so desperate for them to mix? I think we should keep them separate,” says the headmistress from the Londonderry Boys School in the show. Over 90% of schools are “separate” in Northern Ireland, still today. Some teens attend Catholic Maintained schools and other teens attend state-controlled (often majority Protestant) schools. Our research, so far, finds that not only do young people attend different schools, but they may be taught completely different content in different types of schools. In a sample of secondary schools, 96% of Catholic schools teach a class/module on the history of “The Troubles,” compared to only 46% of state-controlled (often majority Protestant background) schools. In a representative survey of young people, a whopping 33% of teens say they were not taught (or did not know if they were taught) about the Good Friday/Belfast Agreement in school. Religious education is also taught as part of the national school curriculum in Northern Ireland, but varies by school type. Studies of the two dominant school types during the Troubles found that they differed in time spent on religious education, rituals, symbols, and general ethos, but more current investigations are needed. Segregation also goes beyond schools into most layers of society. Teens often live in separate neighborhoods or towns, may attend church (Protestant) versus chapel (Catholic), have different hobbies, and read/watch different media. This separation within young people’s microsystems, i.e. their schools, classrooms, and local communities, can create false consensuses that reinforce ingroup perspectives and hinder the potential for cross-pollination and information sharing across group lines.
What may have changed for today’s teens in Northern Ireland since the 1990’s Derry Girls?

A pessimist might say, not much. For instance, the “Protestants are British and Catholics are Irish” narrative on the Derry Girls differences blackboard features prominently in macro-level political discourse today. In the aftermath of Brexit, banners featuring polarized narratives around politics and national identity, like these, are frequent. Such macro-level narratives continue to intersect with micro-level structures, such as what young people learn in school and see in their local communities, leading to divided “truths” or knowledge structures at the individual-level.

But thankfully, we are optimists. Now 25 years post the peace agreement, teens in Northern Ireland have been born into relative peace. Teens are motivated to move forward and continue to correct misinformation transmitted by previous generations: “Macaulay Culkin isn’t a Protestant, Ma!” (Erin, Derry Girls season 1, episode 1). Identities are shifting away from traditional dichotomous categories of Catholic and Protestant. Northern Ireland is secularizing—though it is important to note, not to the same extent as the Republic of Ireland or the rest of the United Kingdom. Teens are more likely to report having “no religion” or being “other” religion, as well as report being “neither” Unionist nor Nationalist. Churches, schools, and youth organizations are contributing to peacebuilding efforts through interfaith dialogue, cross-community initiatives, and integrated and shared education. What we still know less about is how and when young people today are motivated and able to seek out and share reliable information across group boundaries and beyond the limits of traditionally divided societal structures.
Call to Action: A Holistic Lens to Inform Effective Interventions
To navigate the intricate web of old and new, and micro- to macro-level influences on the development of polarization and/or epistemic vigilance in young people, we need innovative methodologies. Here are a few ideas that our team is working on (but we’d love to hear yours too, please comment below!):
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs) emerge as powerful tools to analyze diverse texts, uncovering recurring themes and sentiments that occur in narratives across micro, meso, and macrosystems. This provides a nuanced understanding of the narratives influencing polarization. For instance, what were the Derry Girls learning about history and religion at Our Lady Immaculate College? Based on our current explorations, we have to assume a different history than their counterparts at the primarily Protestant background school down the road. Our team will use NLP to analyze pedagogical resources to understand polarization in history and religion education across Northern Irish classrooms.
- Peer influence is a prominent theme in Derry Girls, pulling at times both towards (e.g., Erin tells her truth, “You can’t marry an Orangeman, Michelle!” Season 1, Episode 5) and away from polarization. Social Network Analysis expands beyond dyadic interactions, exploring naturally occurring social networks within settings like classrooms, local communities, or even more modern-day influences of social media. This approach helps decipher patterns of segregation, intergroup competition, and socialization practices, shedding light on the contextual factors influencing polarized (mis)information.
- Diffusion paradigms, or experimental versions of the game of “telephone,” offer a real-time perspective on information transmission, allowing researchers to track how narratives, both polarizing and unifying, spread across groups. This method opens avenues to study the passing of stories and beliefs across peers, or across generations, contributing to our understanding of the perpetuation or amelioration of intergroup conflict.
Religion has influenced the narratives and perspectives of young people in Northern Ireland through community identity and belonging, education, rituals and commemorations, and moral and ethical interpretations of what is “true.” Employing interdisciplinary, mixed-method research is necessary to holistically explore how truth is defined and produced, how it is evaluated and transmitted at different levels of society, and how to increase epistemic vigilance. By synthesizing findings from various disciplines and methodological approaches, research can inform the development of targeted and effective interventions. These interventions, rooted in a deep understanding of the complexities highlighted in Derry Girls, can empower young people to enhance their epistemic vigilance. Ultimately, the goal is to equip young people with the critical thinking skills needed to catalyze positive social change, fostering healthier, more peaceful, and equitable societies, not only within Northern Ireland but also resonating beyond its borders.
[1] Our research team consists of Jocelyn Dautel (Queen’s University Belfast), Bethany Corbett (Ulster University), Kathleen Corriveau (Boston University), Emma Flynn (Warwick University), Eva Grew (Queen’s University Belfast), Mariah Kornbluh (University of Oregon), Caitlin McShane (Queen’s University Belfast), Jennifer Watling Neal (Michigan State University), Lara Wood (Abertay University), Christin Schulz (University of Amsterdam), and Jing Xu (University of Washington Seattle), funded by Templeton World Charity Foundation.



This replica of the now famous blackboard is on display at the Ulster Museum in Belfast, Northern Ireland.